Product characteristics
Appearance: Dark brown transparent viscous liquid (with green light)
Ionicity: Anionic
PH value: 2-3
Solubility: Easily soluble in water
Stability: Acid, alkali, electrolyte, and hard water resistant
Product features
This product is a color fixing agent for fibers dyed with anionic dyes (acidic dyes, metal complex dyes) used in wool, nylon (nylon), silk, leather, etc. After treatment, the dyed material has improved washing and perspiration fastness.
It has minimal impact on fabric color and hand feel.
It has good acid resistance, which is beneficial for chemical material operations.
How to use
High concentration products can be diluted 2-3 times for use.
Used for color fixing treatment after acid dyes or metal complex dyes dyeing.
The specific dosage should be adjusted by the user through trial samples.
Light color: 1-2% o.w.f
Medium color: 2-3% o.w.f
Dark color: 3-4% o.w.f
Bath ratio 1: 10~15
Temperature & time 80℃× 20min
Mechanism of action
At a lower pH (<2.5), the binding between the dye and the fiber is only van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds. Within the appropriate pH range, the dye binds more firmly to the fiber through ionic bonds, van der Waals forces, and hydrogen bonds, making it less likely to detach. This is why dyeing is chosen under weakly acidic conditions.
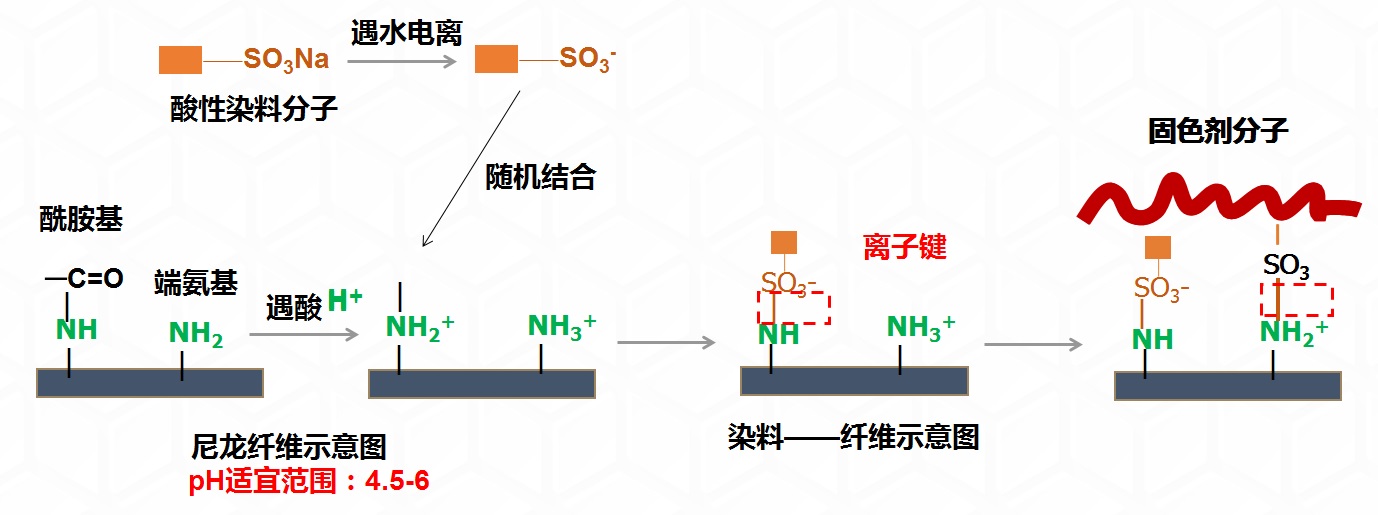
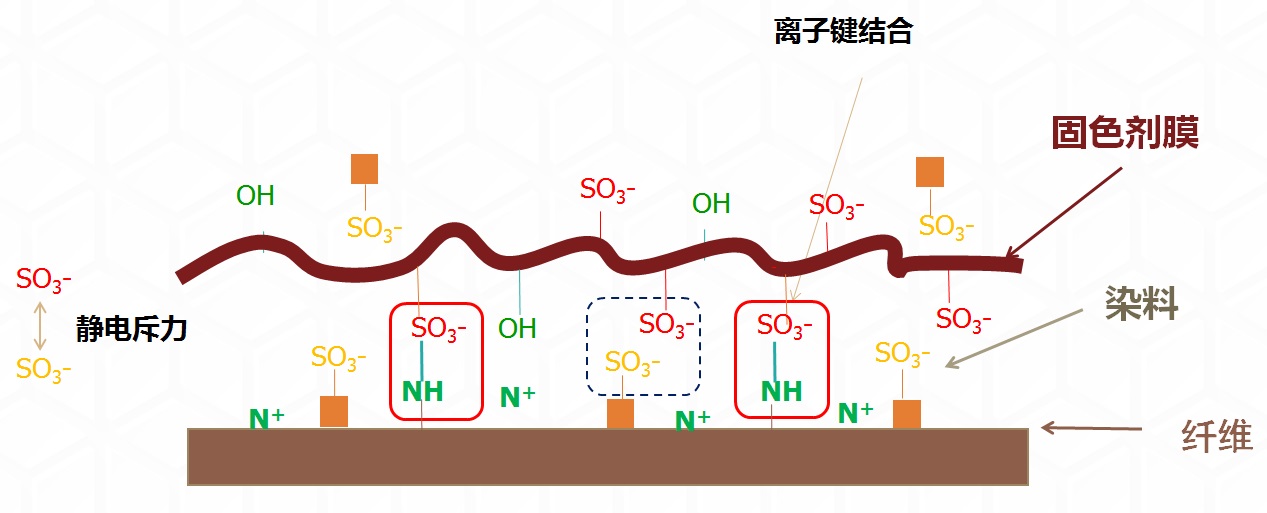
Color fixing mechanism
A composite complex film is formed on the surface of the fiber, blocking gaps, reducing dye diffusion. At the same time, there is electrostatic repulsion between the anions of the color fixing agent and the anions of the acidic dye, hindering the diffusion of the acidic dye into the dye bath and promoting the diffusion of the dye on the fiber surface into the interior of the fiber, reducing the chance of dissolution.
Common problems in color fixing - poor color fastness
Cause analysis
It is caused by the fabric itself. The finer the nylon yarn, the poorer the fastness. The more spandex the fabric contains, the poorer the fastness.
It is caused by the dye itself. Acid dyes come in a variety of types, generally speaking, the more vibrant the color, the smaller the molecular weight, and the poorer the fastness.
Nylon itself has low dyeing affinity, resulting in many dyes not forming strong ionic bonds with the nylon dye seats during deep black dyeing, making the dyes easily dissolved in water.
The color fixing agent itself has no significant effect on improving fastness.
Solution
Ensure that the fabric is thoroughly soaped and remove excess floating color on the fabric surface before dyeing.
Increase the dosage of the color fixing agent appropriately, raise the temperature of the color fixing agent, and lower the pH value of the water bath during color fixing. (Changes in the above process may cause color change, hand feel issues, etc., depending on the actual situation).
In case where achieving high fastness is difficult, a scheme of acid fixing (anionic) - cationic conditioning fixing can be used.
Common problems in color fixing - fixation spots
When nylon is dyed with acid dyes, varying degrees of sticky agglomerates are produced during the fixation process and adhere to the surface of the fabric. After shaping, dark spots (blocks) that are difficult to remove are formed on the cloth surface, called fixation spots.

Cause analysis
High total water hardness
During the dyeing and color-fixing process, when the total hardness of the water is too high or there are too many unknown impurities, it combines with the color-fixing agent to form an insoluble precipitate that adheres to the cloth surface.
Weak cationic additives remaining on the cloth surface
Acidic color-fixing agents are generally high molecular weight aromatic sulfonic acid condensates, which are anionic and will react with residual cationic additives on the cloth surface to produce agglomerates and form color-fixing spots.
Improper operation
When acidic color-fixing agents are mixed with highly concentrated acids, they tend to agglomerate and produce precipitates. When color-fixing, they adhere to the cloth surface to form color-fixing spots. When mixing materials, feeding the highly-concentrated color-fixing agents before they are completely dissolved can also easily cause color fixation. spot.
Solution
Use dyeing water with good water quality.
Use a leveling agent or fixing agent with good compatibility.
Wash before dyeing to reduce cation residues.
Pay attention to the order of feeding and avoid direct contact with highly concentrated acid.
Common problems in color fixation—discoloration after color fixation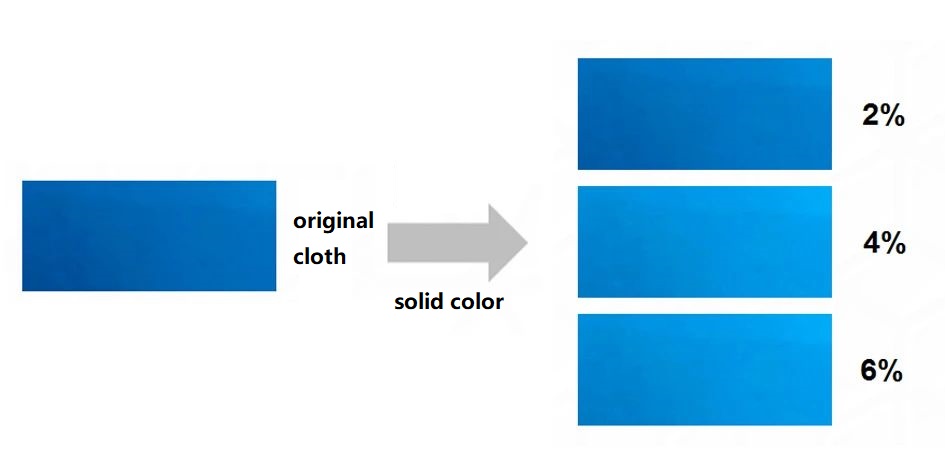
Cause analysis
Changes in dye structure: Some colors, such as Cuilan, are sensitive to acids. If the pH is too low, the dye structure will be destroyed.
The appearance of the fixing agent itself may add color to the fabric.
The color-fixing agent changes color when oxidized. The color-fixing agent itself contains easily oxidizable groups, which are easily oxidized and cause color change.
It depends on the dosage. The greater the dosage of color-fixing agent, the easier it is to produce discoloration.
Application performance - wash fastness
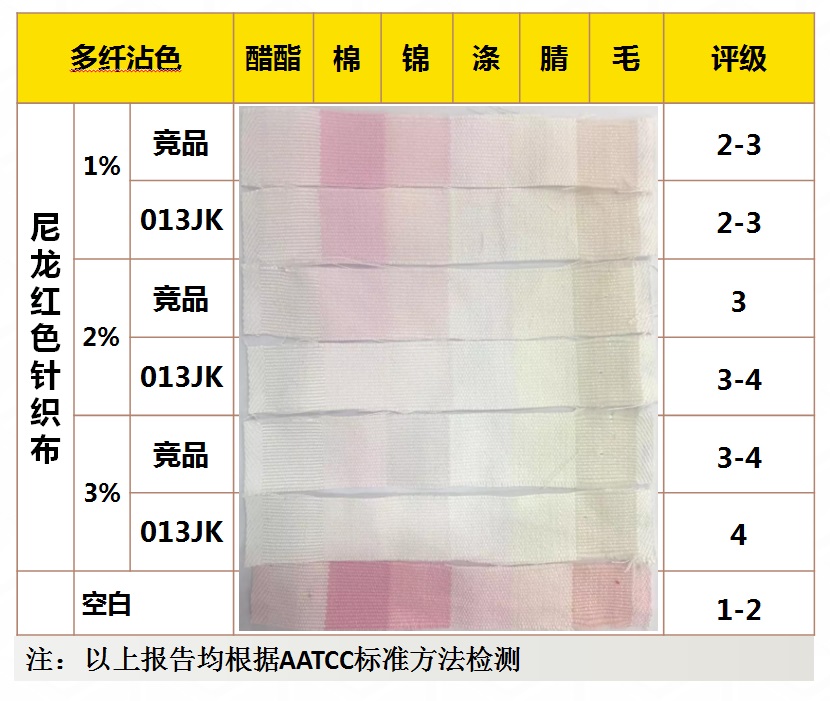
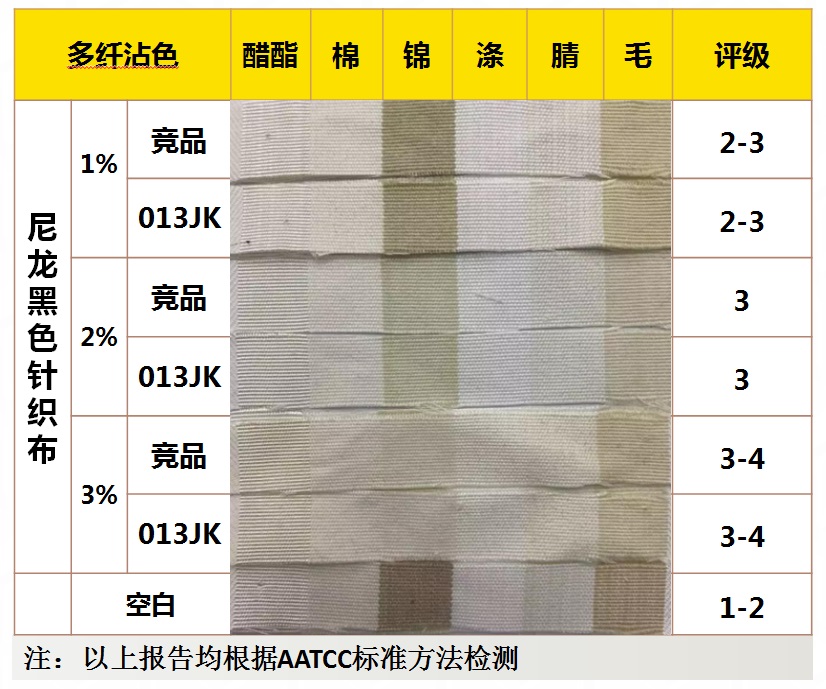
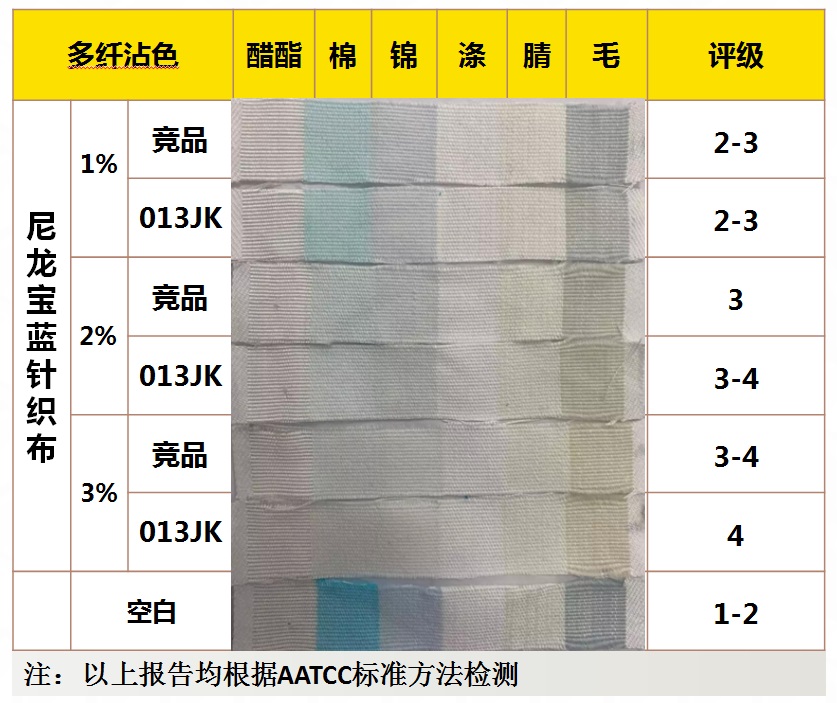 Application performance - water fastness
Application performance - water fastness
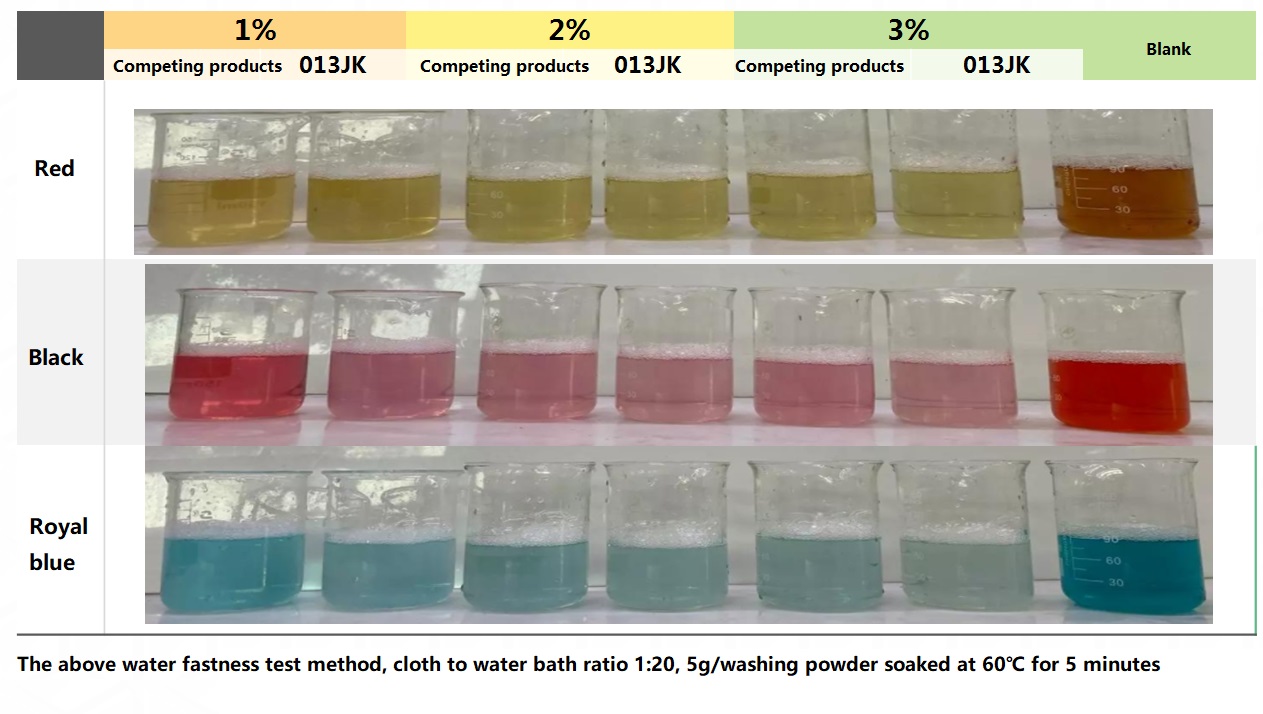

Solubility in the same bath
Mixed with a high concentration of degreaser (non-ionic), 013JK still remains clear.
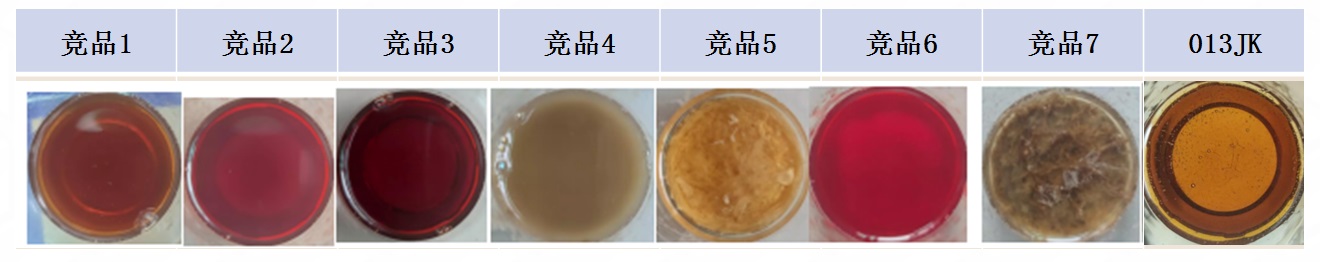
In the same bath with our zwitterionic acid leveling agent:
After boiling leveling agent + acid fixing agent, 013JK still remains clear.
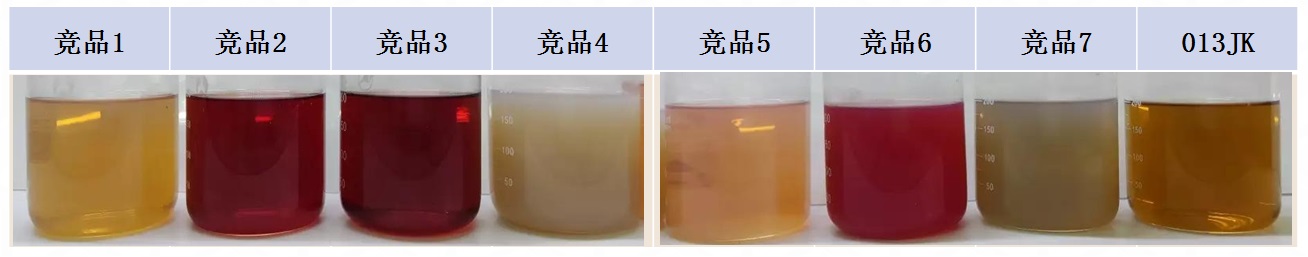
Performance summary
No acid adjustment is required to avoid fixation spots caused by operation.
It has good fastness and can significantly improve the color fastness.
Does not contain harmful substances.
It has good compatibility with leveling agents and degreasers, reducing the appearance of color-fixing spots. (Subject to actual test data)



 English
English  日本語
日本語  Español
Español  tiếng việt
tiếng việt  Türkçe
Türkçe  ไทย
ไทย  українська
українська  हिंदी
हिंदी  বাঙালি
বাঙালি  اردو
اردو