This article introduces the performance comparison of several textile printing auxiliaries. Let us take a look:
1. Determination of defoaming performance of dyeing auxiliaries
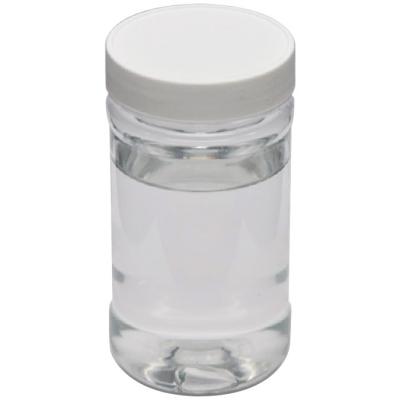
Take two test tubes with stoppers of the same size (preferably more than 20ml), add the same amount (such as 10ml) of the tested sample, and shake them up and down 20 times. The time required for the foam to collapse completely is the defoaming time. The shorter the defoaming time is and the faster it deforms, the better the defoaming performance is.
2. Determination of acid resistance of dyeing auxiliaries
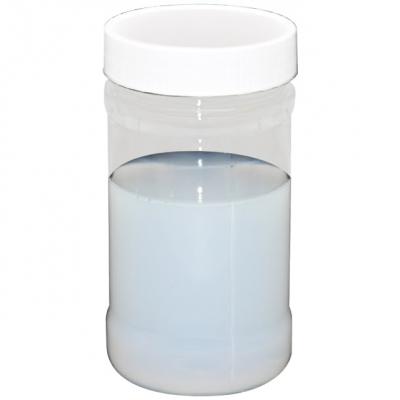
Take several beakers of the same size, add the same amount (such as 100 grams) of the sample of dyeing auxiliaries to be tested, and then add 5 grams of glacial acetic acid to the beaker and stir evenly. Observe whether there is turbidity or layering. The amount of acetic acid added in the turbid or layered beaker is the acid resistance.
3. Determination of alkali resistance of dyeing auxiliaries
Take several beakers of the same size, add the same amount (such as 100 grams) of the tested sample, and then add the caustic soda (or soda ash) solution to the beaker in increments of 5 grams and stir evenly. Observe whether there is turbidity or stratification. The amount of caustic soda (or soda ash) solution in the beaker where turbidity or stratification occurs is the alkali resistance.
4. Determination of electrolyte resistance of dyeing auxiliaries
Take several beakers of the same size, add the same amount (such as 100 grams) of the tested sample, and then add the electrolyte solution to the beaker in increments of 5 grams and stir evenly. Observe whether there is turbidity or stratification. The amount of electrolyte solution added in the beaker where turbidity or stratification occurs is the electrolyte tolerance.
The electrolyte is generally selected from magnesium chloride, sodium chloride, etc., It can also be selected according to actual needs.
5. Determination of hard water resistance of dyeing auxiliaries
Hard water resistance is similar to electrolyte resistance. The result of choosing calcium chloride and magnesium chloride as electrolyte is hard water resistance. For ease of use, the concentration of the electrolyte-resistant solution can be converted into the hardness of water.
Permeability test of dyeing auxiliaries: Prepare the tested sample into a test solution according to a certain concentration, and place the standard canvas sheet horizontally on the surface of the test solution. The time from when the canvas sheet sinks to the bottom of the cup indicates the permeability of the tested sample.



 English
English  日本語
日本語  Español
Español  tiếng việt
tiếng việt  Türkçe
Türkçe  ไทย
ไทย  українська
українська  हिंदी
हिंदी  বাঙালি
বাঙালি  اردو
اردو